Learn how to set up software translation projects in PTC. Step-by-step guide to creating projects, uploading files, and getting AI translations in minutes.
Step 1
Sign Up for PTC
Create your account to start a free trial that lets you translate 20,000 words into 2 languages.
Step 2
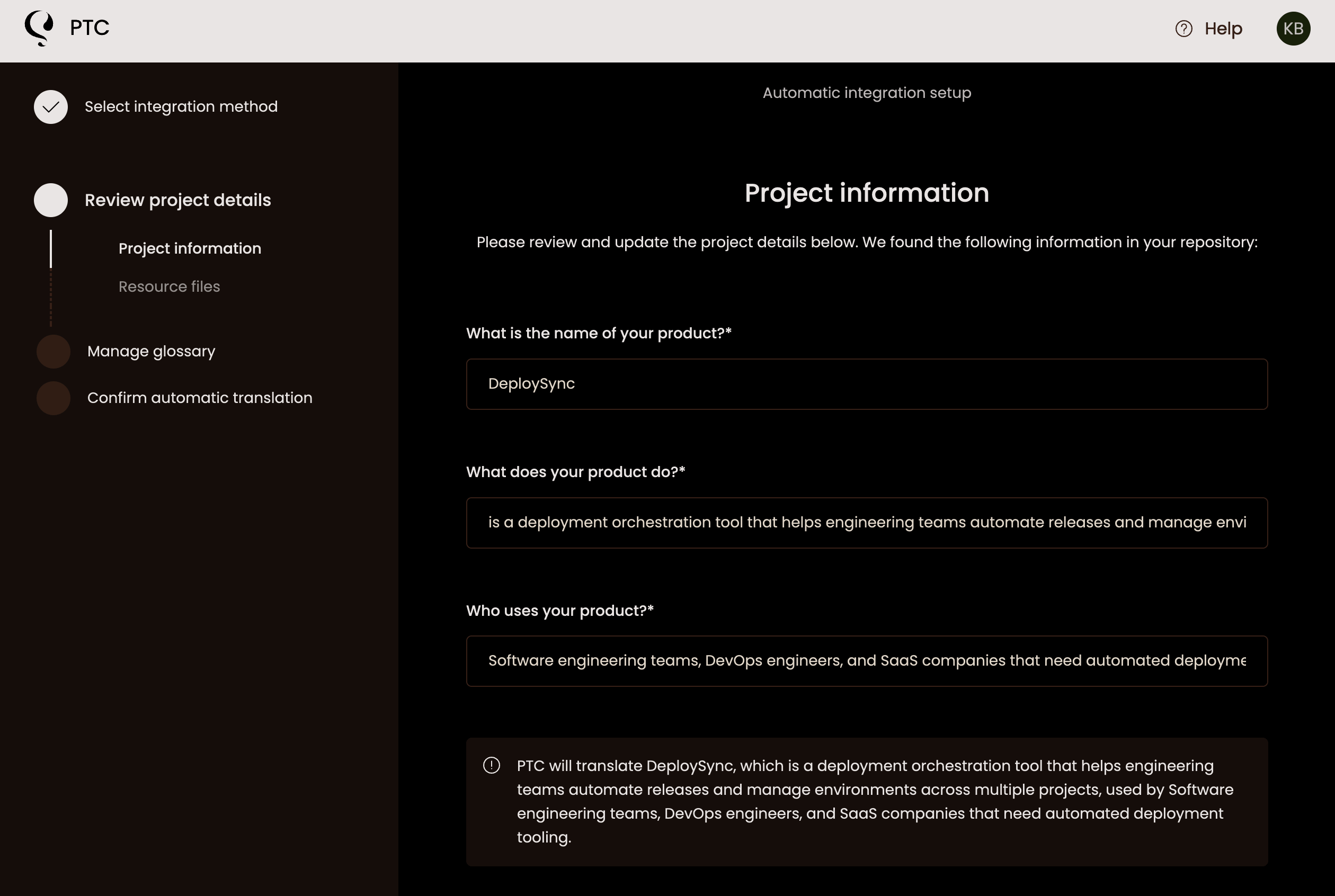
Add Project Information and Select Languages
In the setup wizard, enter your product name, target audience, and terminology preferences. This context influences the tone and formality of your translations.
Then choose which languages to translate into. PTC supports 33+ languages. During the free trial, you can select up to 2 languages.

Step 3
Upload Your Resource Files
Upload the files containing your translatable text. PTC can translate a wide range of resource file formats, including:
Gettext.po
JSON
YAML
Adobe Commerce / Magento .csv
Android
Apple .strings
Apple .stringsdict
Apple .xcstrings
Java Properties
JSON Array
See all supported file formats →
Step 4
Add Glossary Terms (Optional)
PTC automatically adds your product name to the glossary. Add any brand terms that require specific translations to ensure consistency across your project.
You can manage glossary terms at any time from the Glossary tab in your dashboard.
More about the glossary in PTC→
Step 5
Get Your AI Translations
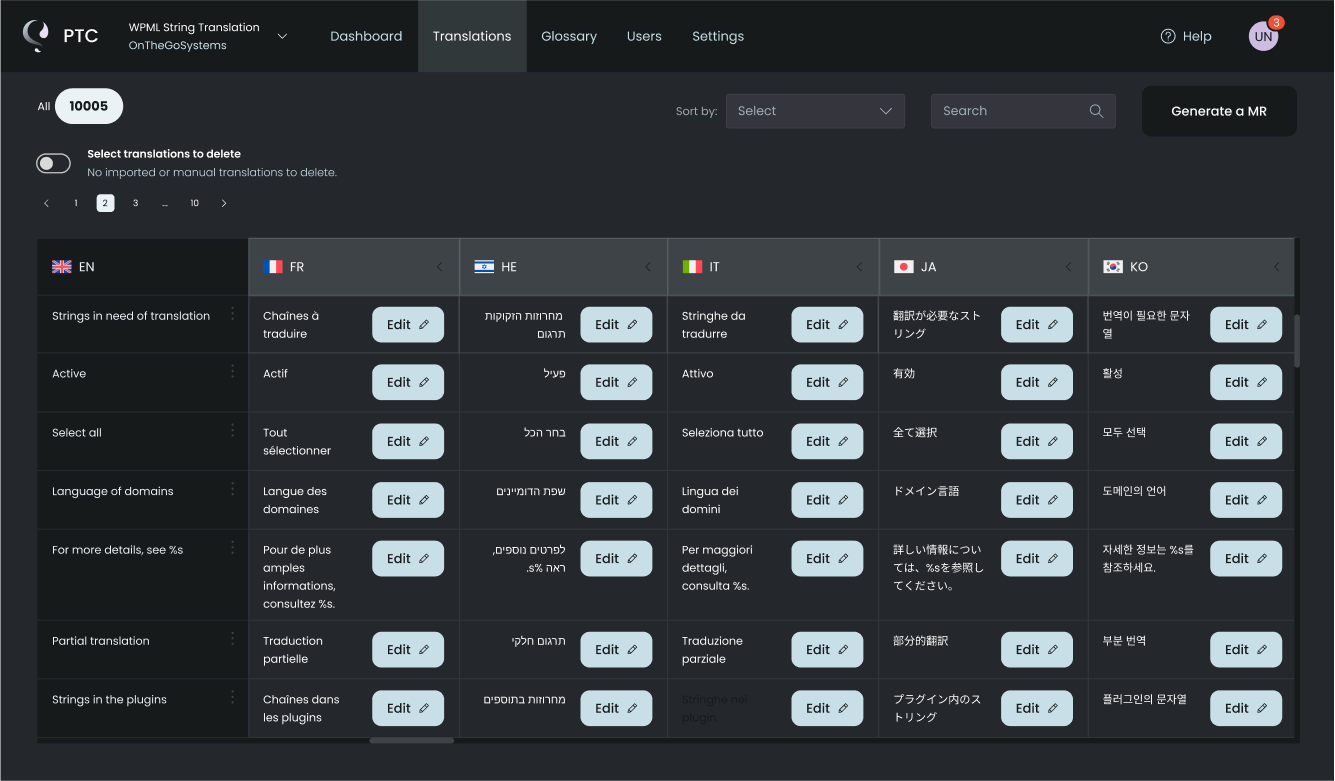
Once setup is complete, PTC automatically translates your files. You can download a ZIP from the Resource files tab, or view and edit translations in the Translations tab.
Set Up a Continuous Localization Flow
After completing your initial project setup, you can connect PTC to your development workflow for ongoing, automated localization.

Git Integration
Connect PTC to your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repository so that PTC monitors for updates and delivers translations via merge requests. This integration method requires you to grant PTC read and write access to your repository and add your access token.
To set this up, go to Settings → Branch Management and click Add Git integration. You’ll be prompted to choose your repository provider. All the project information and languages you already configured will be pre-filled.
For step-by-step instructions on connecting your repository, see the integration guides:

API Integration
Integrate localization directly into your CI/CD pipeline using the PTC REST API. The API lets you add and update source files, retrieve information, manage translations, and more.
To get started, go to Settings → Manage API Tokens and click Add access token to generate your token. Then follow the PTC API Reference to integrate software localization into your development process.