Easy JSON file translation in minutes with the most accurate JSON translator. Upload your resource file and download translations to localize your project.
How To Translate a JSON File
PTC can translate JSON files into 35 languages.
Step 1: Sign up Free and Create a New Project
Sign up without a credit card to start a free trial with PTC — a highly accurate AI Translator for JSON files and other file formats. The 30-day trial lets you translate 20,000 words into two languages.
Step 2: Fill Out Product Context And Languages
Right after signing up, you will go through a 5-minute setup wizard:
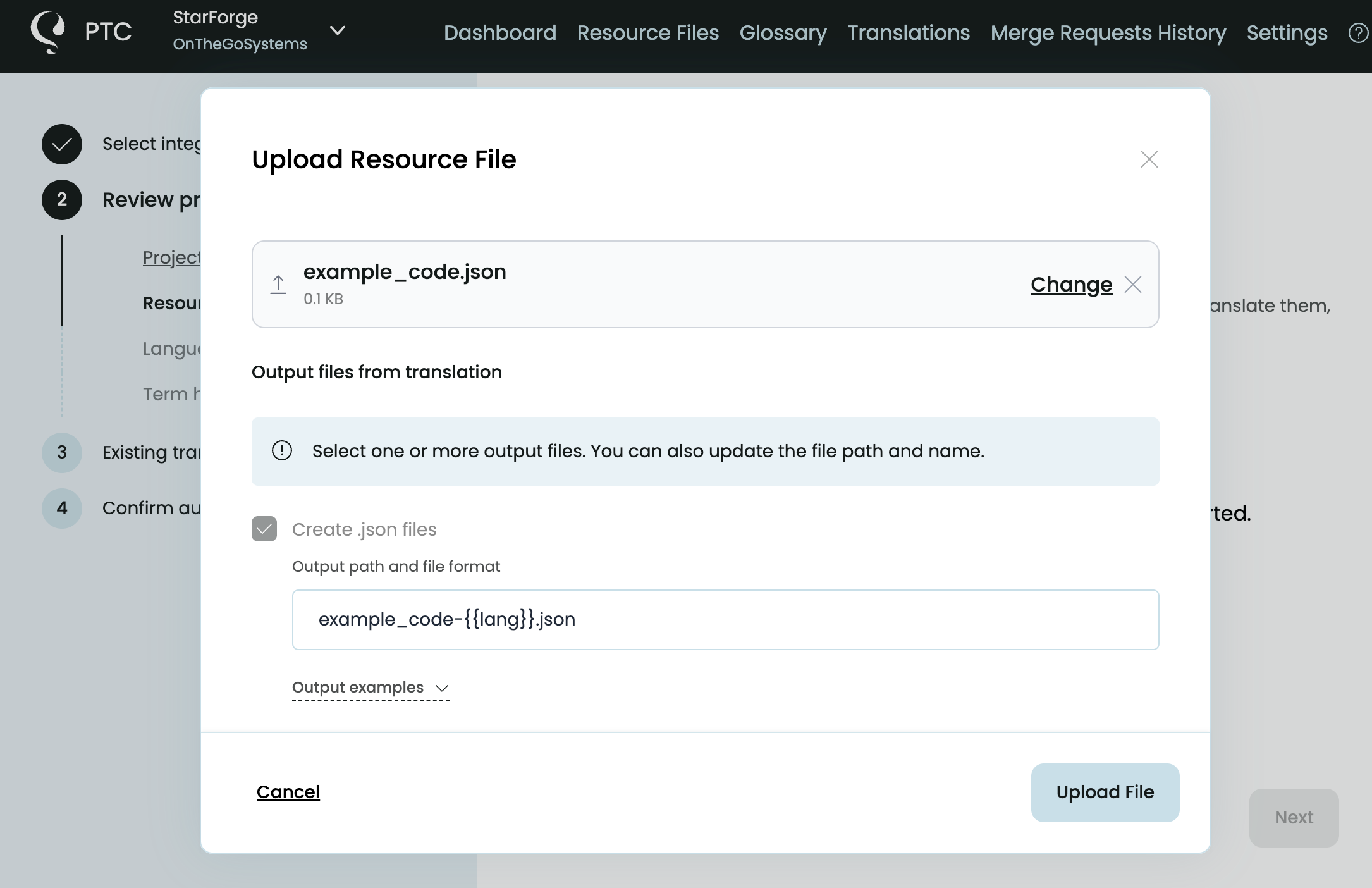
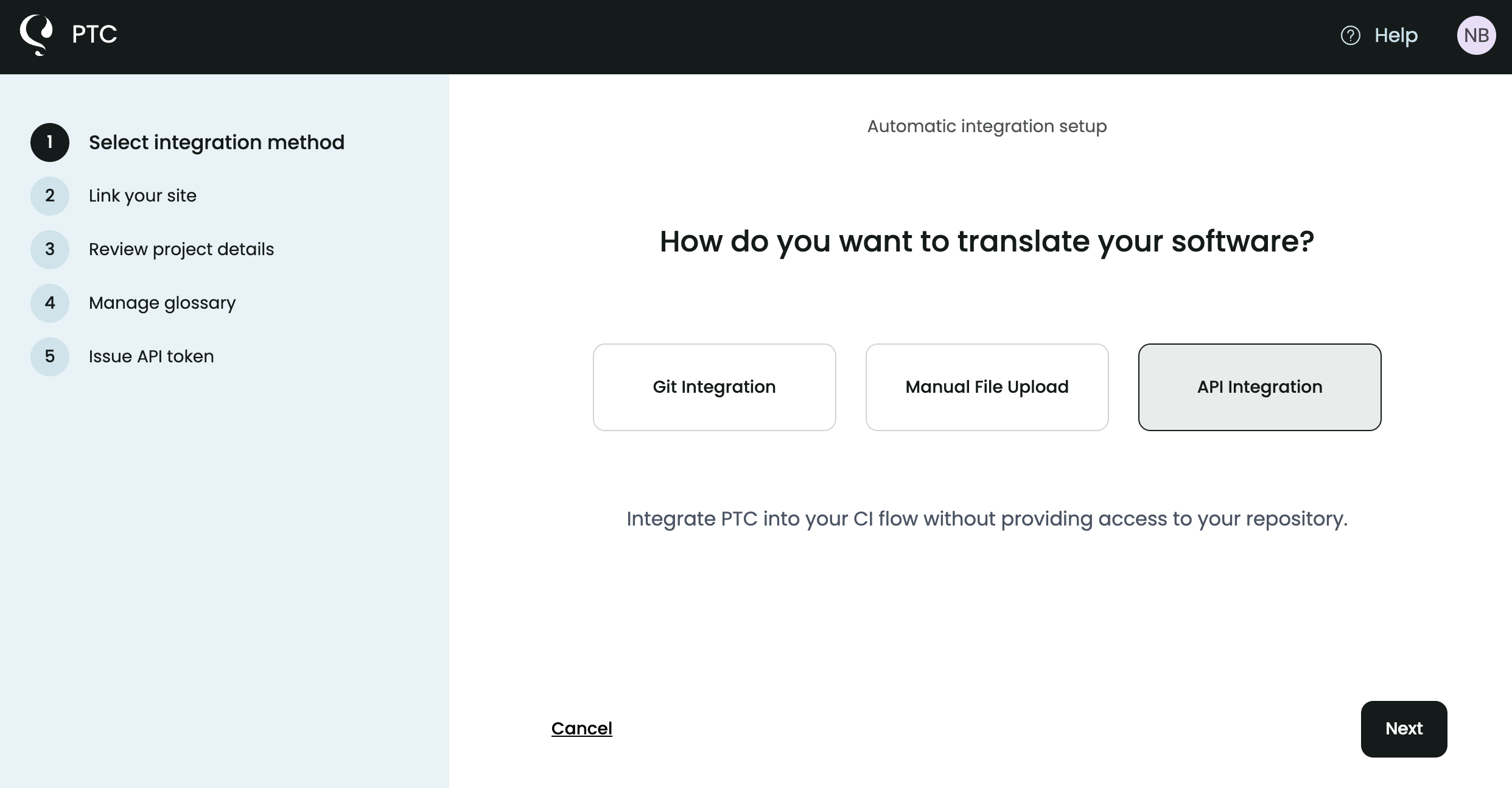
- Upload your JSON files and update the file path and name, if you want.
- Tell PTC what your JSON files are for (e.g. a React app).
- Select target languages from 30+ languages available.
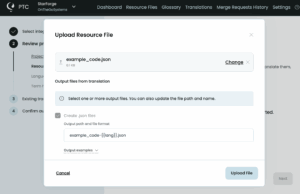
PTC will use the product description you provide and the context of your file and app to apply the right terminology and tone to translations.
Step 3: Download and View Translated JSON Files Free
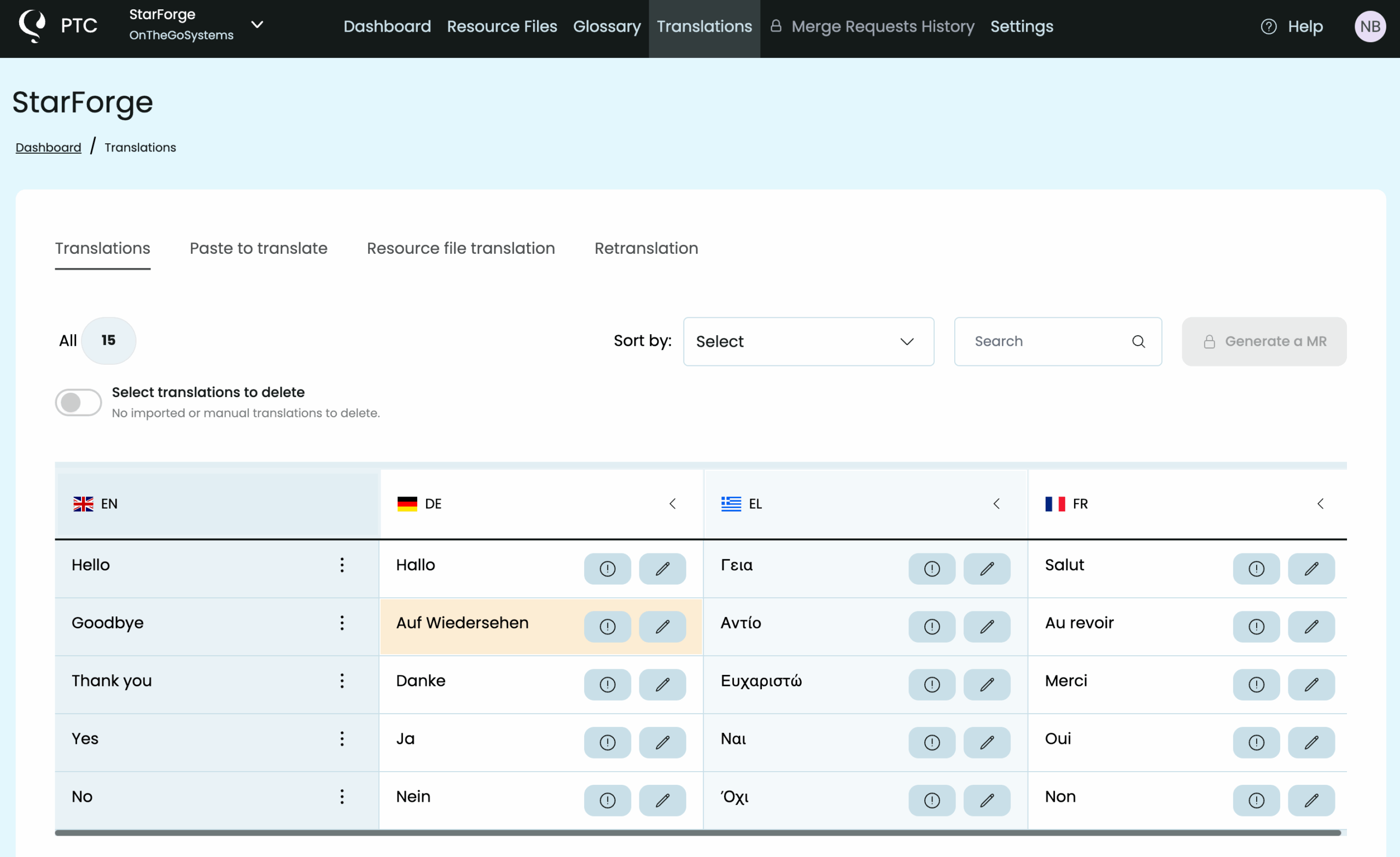
PTC finishes translations in minutes and you can download them in a ZIP file immediately. You can also click on View translations to see the results in a neatly organized table. You keep already generated translations even when your free trial ends.
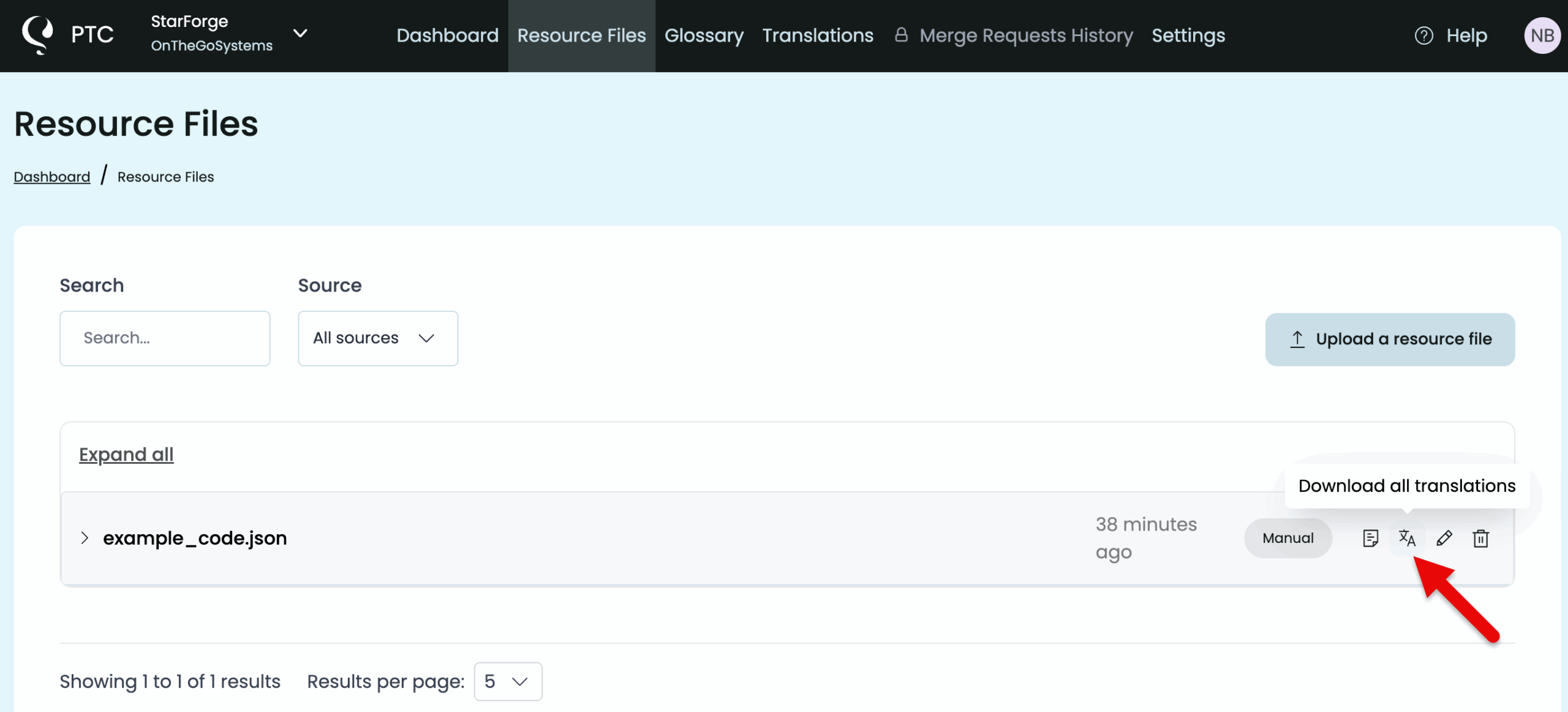
Download or re-download your translated files from the Resource Files tab at any time.
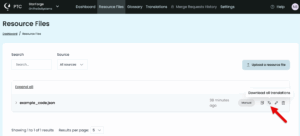
For future translations, you can adjust file paths, branches, or placeholder formats, by going to Settings in your PTC dashboard. If you need to translate more files, go to Billing and payment to activate Pay-As-You-Go and only pay only when you translate.
Auto translate JSON Files
You don’t need to manually upload single JSON files every time you change something in the code. You can automate the JSON file translation process: PTC can connect to your repository and monitor changes to your resource files to keep translations updated over time.
Option 1
Automate with Git Integration
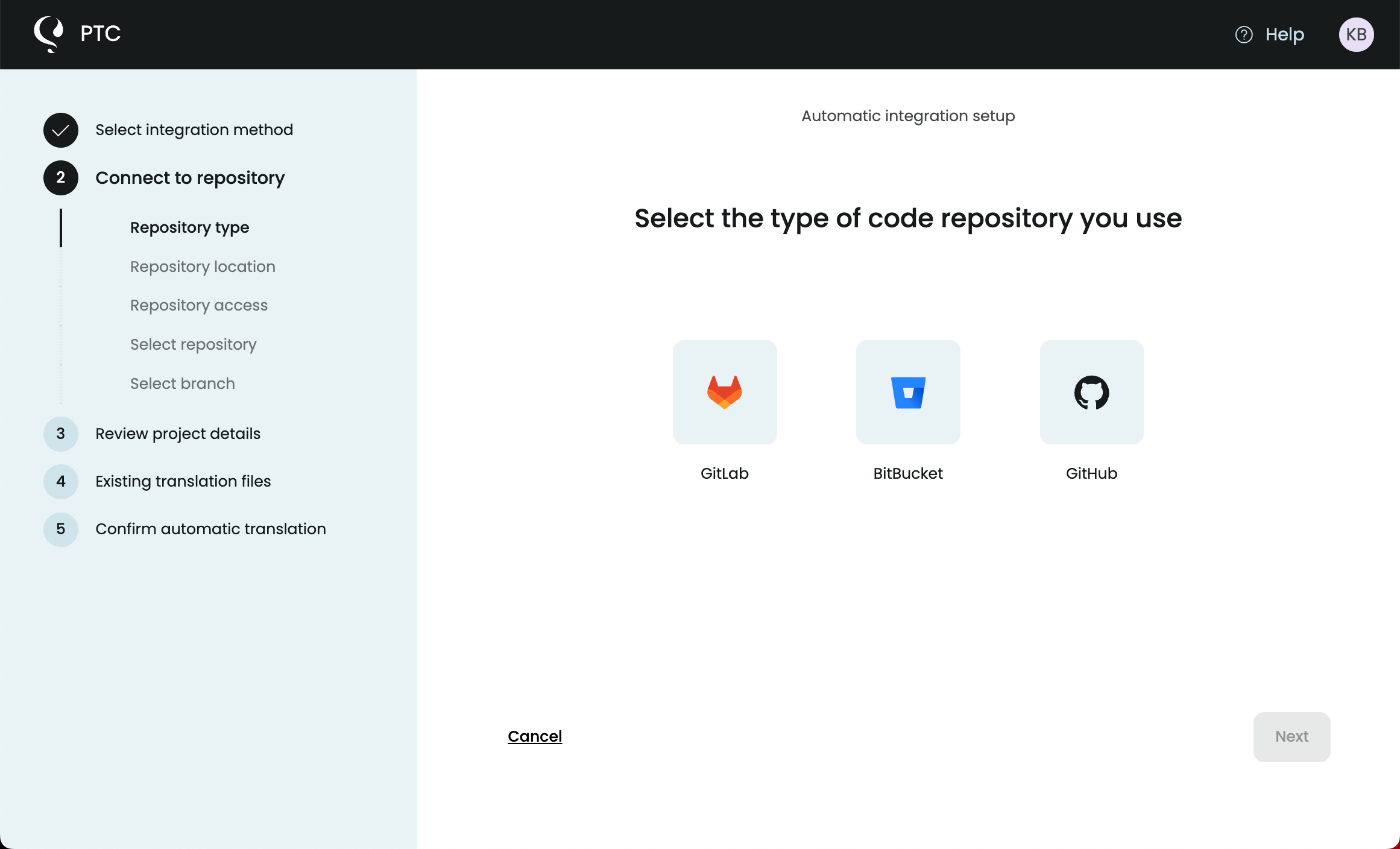
To move your existing project to Git integration, go to Settings → Merge requests and click Add Git integration. This will allow you to connect your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repository to PTC. In the setup wizard, you will need to:
- Connect your repository with an access token with read and write permissions.
- Select branches you want PTC to monitor.
PTC detects changes, translates new strings, and sends you a merge request.
Option 2
Automate with PTC’s API
The PTC API lets you integrate translation into your CI/CD pipeline. This method is great if you don’t want to allow access to your repository directly.
You can move your existing project to CI/CD integration by going to Settings → Manage API tokens. Click Add access token to generate a token, then see the complete API documentation for all endpoints.
For subsequent projects, simply choose API Integration at the beginning of project setup.

Use The Most Reliable AI Translator For Any Localization Project
PTC delivers accurate, natural-sounding translations for any app, software, or resource file format. Start your free trial and reach global audiences with ease.