When used correctly, AI can translate your software at human quality. Follow this guide to achieve natural and consistent AI translations to any language. Each step includes real examples, so you can see exactly what works best and why.
1
Make Your UI Texts Clear and Easy to Understand
PTC translates exactly what you put in your resource files. Clear, complete sentences in the original language give it the context it needs to preserve the exact meaning in every translation.


Example of a clear string
You have no saved items in your cart.This sentence tells the user what’s empty (“cart”) and what it contains (“saved items”), giving PTC full context to produce an exact translation.

Example of an unclear string:
No cart items.This leaves out the subject (“you”) and the action (“have”). In some languages, it could translate to “There is no cart” instead of “Your cart is empty,” which changes the meaning.

When you write complete sentences, fix typos, and use simple words, you help PTC to deliver translations that are natural and easy for your users to understand. User feedback on translations can help you identify what to improve in your texts.
2
Describe Your Product and Audience in Detail
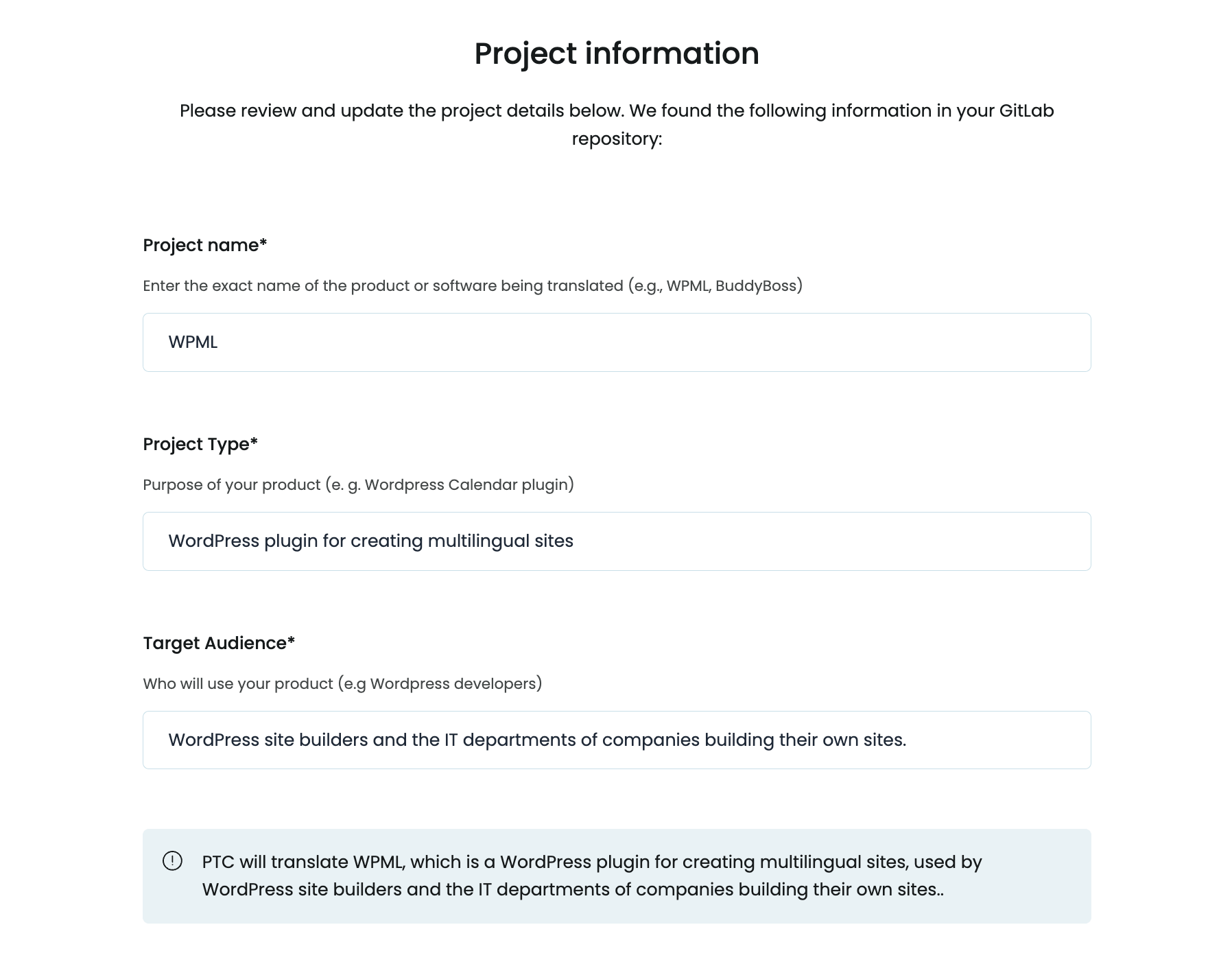
When you set up a project in PTC, you’ll enter:
- The name of your product
- What it does
- Who it’s for
PTC uses this to select the right terminology, tone, and style so your translations match your product’s purpose and audience.


Example of good product information:
| Product Name | What It Does | Audience |
|---|---|---|
| WPML | A WordPress plugin for creating multilingual sites | WordPress site builders and IT departments |
This description includes enough context for PTC to be able to choose accurate technical terms and match the tone to your users.

Example of bad product information:
| Product Name | What It Does | Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Wpml | multilingual plugin | users |
This leaves out your platform and audience details. PTC has less background information to work with, so translations may sound too generic or use the wrong formality.

3
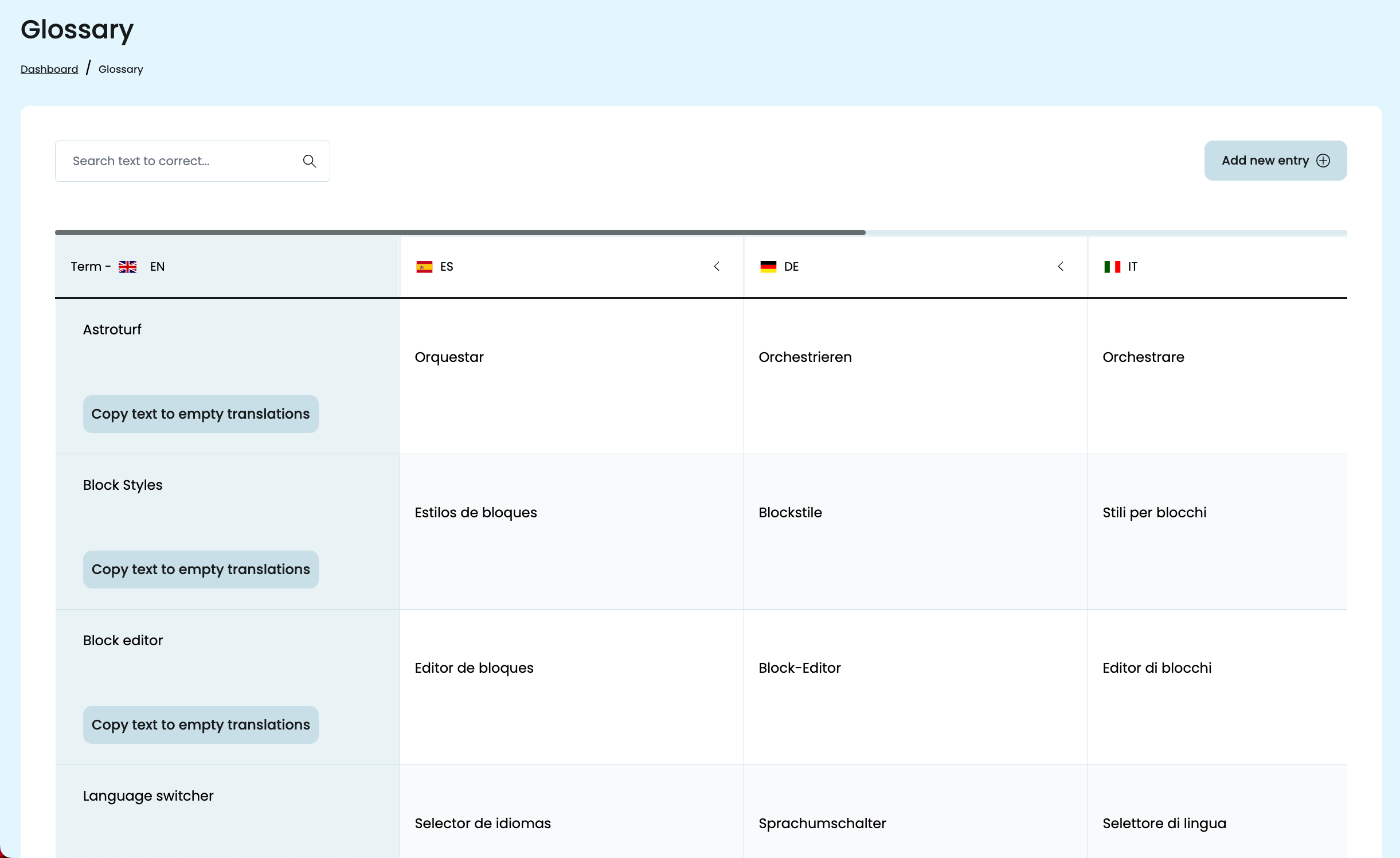
Add Important Product Terms to the Glossary
PTC automatically adds your product name to the built-in glossary so it’s never translated. You only need to add terms that are unique to your product or brand, or that might have multiple meanings in other languages. This keeps the translation consistent in every language.
Example: If your app has a feature called Spaces, you wouldn’t want it translated into the generic word for “rooms” or “areas.”
Adding “Spaces” to the glossary with a description like “A branded collaboration feature for team projects” tells PTC to treat it as a proper name and use the correct term in every translation.
A well-maintained glossary keeps your terminology consistent across your entire product, so users see familiar and correct wording in every language.
4
Use Placeholders for Dynamic Text
Using placeholders lets PTC translate the full sentence at once, even when it includes variables like usernames or numbers.
For example, let’s say you want to speak directly to your users and dynamically show how many unread messages they have. Your user might see something like:
Welcome Steve, you have 7 new messages.


In PHP, here’s what this should look like:
printf( __( 'Welcome %s, you have %d new messages.', 'text-domain' ), $username, $message_count );
PTC sees one complete sentence and can place the name and number in the correct position for each language.

If you don’t use placeholders and instead concatenate this text from several strings, like this:
echo __( 'Welcome ', 'text-domain' ) . $username . __( ', you have ', 'text-domain' ) . $message_count . __( ' new messages.', 'text-domain' );
PTC will see separate fragments, which makes it harder to rearrange words correctly in languages with different grammar rules.

Placeholders ensure your translations are natural, accurate, and grammatically correct in every language.
5
Design Your UI for Different Text Lengths
When text is translated, it often becomes longer or shorter than the original. A flexible design ensures your user interface still looks good and functions properly in every language.
Here’s a real-world example from a climbing wall:
- English: Beware, climber above
- Spanish: Cuidado, hay alguien escalando sobre ti
Both versions sound natural in their language, but the Spanish text takes up more space. The same thing happens in software. A button label, error message, or menu item that fits in English might overflow or wrap awkwardly in another language.
By using a responsive layout and testing your UI in multiple languages during development, you can make sure text fits well and your design looks clean and polished in all language versions of your application.

Ready to translate with AI?
Put these best practices to work and get human-quality AI translations that sound great in every language! Start your free trial with 2,500 words translated into 2 languages, then pay only for what you translate.