Translate XML files instantly with AI. Upload strings.xml of any size to our Android string translation tool and localize your app in minutes.
20,000 words for free
Easy, 5-minute setup
Context-aware translations
Get Started with Android Strings XML Translation
Step 1
Sign Up To Use PTC for Free
Sign up for a PTC account for a free 30-day trial that lets you translate 20,000 words into 2 languages. Once you use the trial word limit, you can activate Pay-As-You-Go and pay only for what you translate.
Step 2
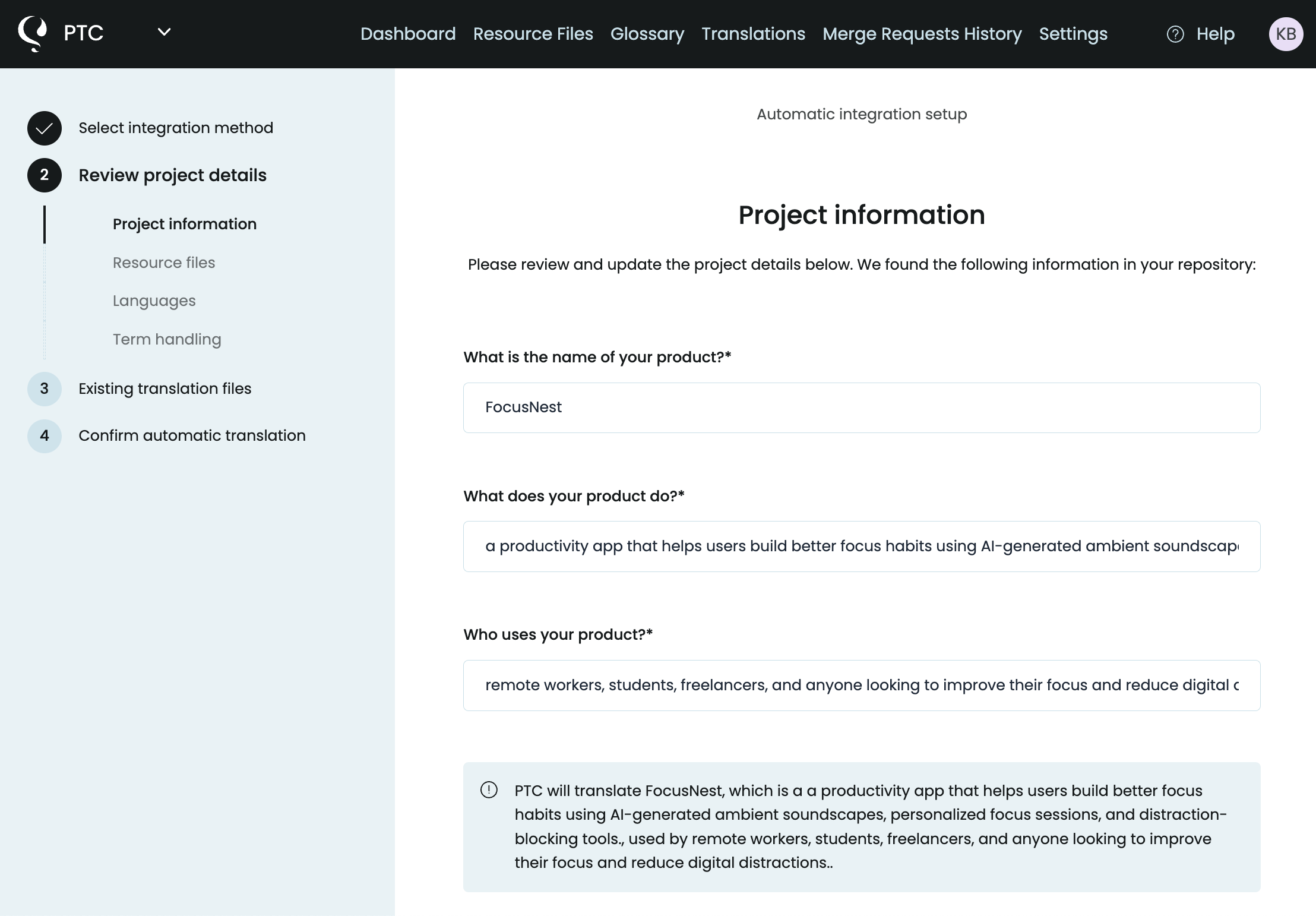
Set Up Your Project and Upload the strings.xml File
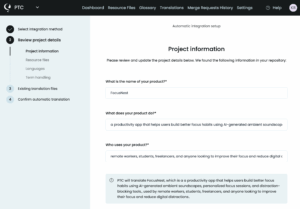
Go through PTC’s setup wizard to:
- Tell PTC about your Android app. Unlike generic tools like ChatGPT, Google Translate, or DeepL, PTC uses this information to generate translations that sound natural.
- Select your target languages
- Upload your
strings.xmlfile
Step 3
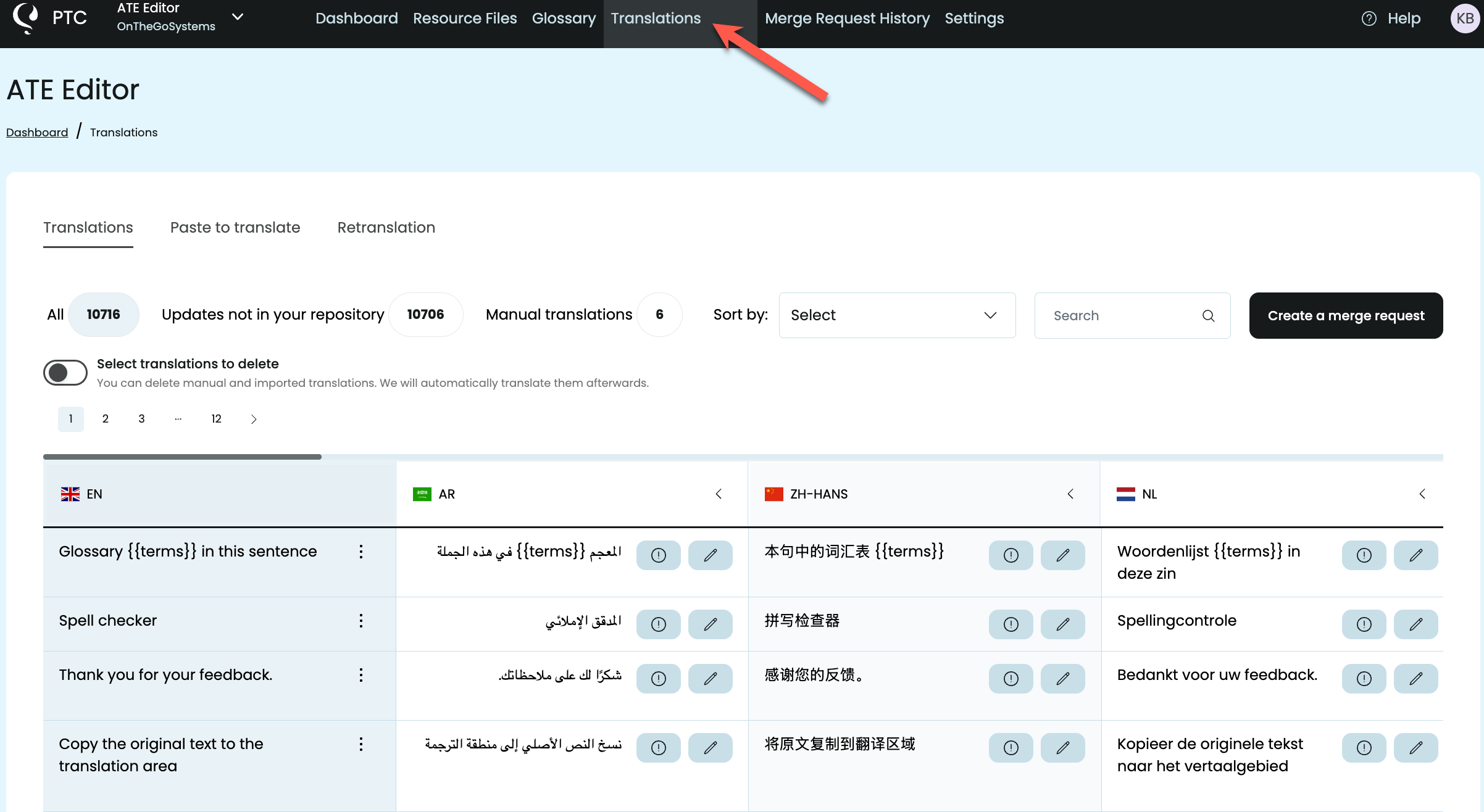
Download the Translated Files
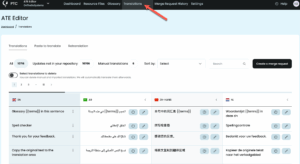
Once translation is complete, view all your strings in the Translations tab. You’ll notice that all your technical elements—like %s, %d, %1$s, and XML tags—appear exactly as they did in your original file. PTC automatically recognizes and preserves these placeholders, so your translations won’t break your app’s formatting or functionality.
PTC also highlights translations that are too long in yellow, making it easy to spot potential UI issues. You can:
- Edit translations directly yourself
- Ask PTC to retranslate specific strings to meet a length requirement
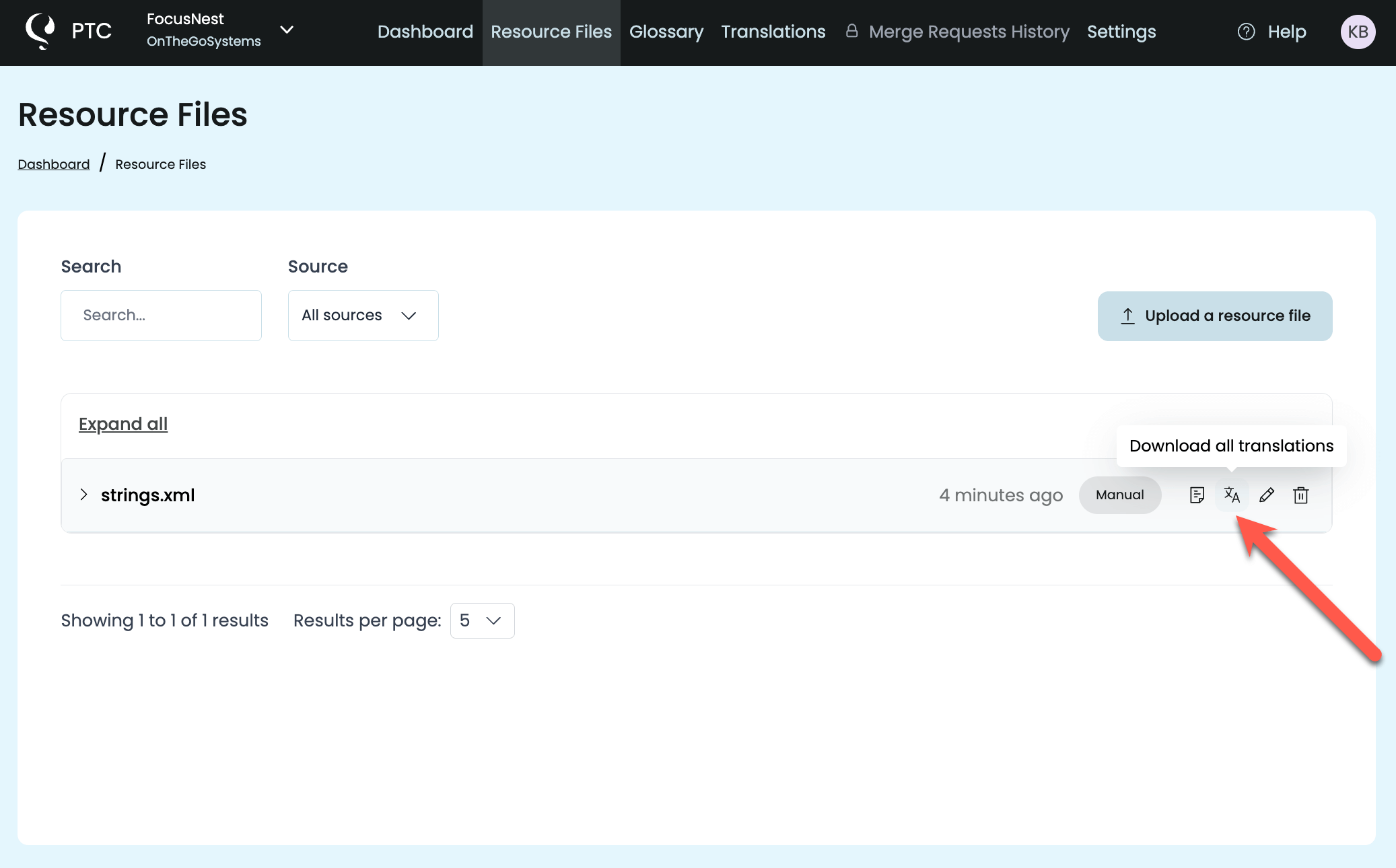
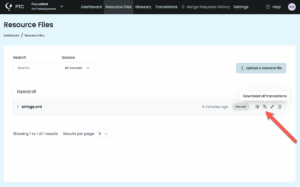
When you’re ready, go to the Resource Files tab and download a zip archive. The zip contains one translated strings.xml file per language, maintaining the exact same format as your original file.
Adding Translations to Your Android Project
To use the translations in your project, create localized values folders for each language using the correct ISO 639-1 language code:
/res
/values <!-- Default (English) - REQUIRED -->
strings.xml
/values-es <!-- Spanish -->
strings.xml
/values-de <!-- German -->
strings.xml
/values-uk <!-- Ukrainian -->
strings.xml
Place the corresponding translated strings.xml file from your downloaded zip into each folder.
Always include a default values folder (without a language code) that contains strings.xml. This is your fallback – if Android can’t find a translation for the user’s language, it uses this one.
Once your translated strings.xml files are in place, rebuild your app. Android will automatically display the correct language based on the user’s device settings.
Implementing Language Switching (Optional)
If your app includes a language switcher so users can change the language independently of their device settings, you need to save their choice and apply it every time the app starts.
Here’s how to change the language when a user selects a different one:
fun setLocale(context: Context, languageCode: String) {
// Save the user's choice
val prefs = context.getSharedPreferences("Settings", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
prefs.edit().putString("app_language", languageCode).apply()
// Apply the new locale
val locale = Locale(languageCode)
Locale.setDefault(locale)
val config = Configuration()
config.setLocale(locale)
context.resources.updateConfiguration(config, context.resources.displayMetrics)
// Restart the activity so changes take effect
if (context is Activity) {
context.recreate()
}
}Then, in your Application class or main activity’s onCreate(), load the saved language preference:
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val prefs = getSharedPreferences("Settings", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
val languageCode = prefs.getString("app_language", "en") ?: "en"
val locale = Locale(languageCode)
Locale.setDefault(locale)
val config = Configuration()
config.setLocale(locale)
resources.updateConfiguration(config, resources.displayMetrics)
}This saves the user’s language choice so it stays the same every time they open the app, and it works correctly after you publish your app to Google Play.
Moving to Continuous Localization for Android
Instead of uploading your strings.xml file manually each time, you can automate the translation process. PTC can connect to your repository and keep translations up to date as your files change.
Option 1
Automate with Git Integration
Go to Settings → Merge Requests and click Add Git Integration to connect your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repository to PTC. During setup, you will need to:
- Connect your repository using an access token with read and write permissions.
- Choose the branches you want PTC to monitor.
PTC will detect changes, translate new strings, and open a merge request for your review.
Option 2
Automate with PTC’s API
The PTC API lets you plug translation into your CI/CD pipeline — a good option if you’d rather not grant direct repository access.
If you’ve been uploading files manually, switch to CI/CD integration by going to Settings → Manage API Tokens and clicking Add Access Token. Then check the complete API documentation for all endpoints.
For subsequent projects, select API Integration at the start of project setup.
Frequently Asked Questions about Android Localization
How do I translate my app description for Google Play?
Use the “Paste to translate” feature from PTC. Copy your app description, paste it into PTC, select your target languages, and get translations instantly.
You can then copy the translated descriptions and add them directly to Google Play Console:
1. Go to Google Play Console → Store Presence → Main Store Listing → Translations
2. Add your translated short and long descriptions
3. Save your changes
4. Repeat for each language you want to support
Should I use string resources or hardcode text in my Android app?
Always use string resources stored in strings.xml files—never hardcode text directly in your code or layouts. String resources make localization possible. You can’t translate text that’s hardcoded in Kotlin or Java files.
Move hardcoded text to res/values/strings.xml:
<resources>
<string name="welcome_text">Welcome to our app!</string>
</resources>Then reference it in your code:
val welcomeText = stringResource(R.string.welcome_text)See our demo app commit: Extracting hardcoded text to strings.xml.
How do I handle placeholders like %s and %d in strings?
Define placeholders in your strings.xml file using %1$s (for strings), %2$d (for integers), etc:
<resources>
<string name="welcome_user">Welcome, %1$s!</string>
<string name="points_summary">%1$s, you have %2$d points.</string>
</resources>
Use them in your Kotlin code:
val welcome = stringResource(R.string.welcome_user, userName)
val summary = stringResource(R.string.points_summary, userName, points)
PTC automatically recognizes and preserves these placeholders during translation.
See our demo app commit: Adding placeholder-based string for dynamic text.
How do I handle right-to-left (RTL) languages like Arabic or Hebrew?
Use start and end instead of left and right in your layouts:
<!-- Instead of this -->
<TextView
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp" />
<!-- Use this -->
<TextView
android:layout_marginStart="16dp" />Android automatically flips the layout for RTL languages when you follow this convention. In Jetpack Compose, use Arrangement.Start instead of Arrangement.Left.
How do I test my localized Android app?
Change your device language in Settings, or use Android Studio’s emulator language picker. Test each language to catch:
– Text that’s too long for UI elements
– Missing translations (falls back to default language)
– Incorrect date, number, or currency formatting
– Layout issues with longer text
For RTL languages, enable “Force RTL layout direction” in Developer Options to test layout mirroring.
Try PTC for free
Want to see PTC’s translation quality and ease of use first-hand? Sign up for the trial and translate 20,000 words into 2 languages for free.